If you have a skin condition that you are finding difficult to treat or control, then you might be offered a course of phototherapy to help ease it.
This is commonly used to treat issues such as psoriasis, eczema and acne, and has also entered the world of beauty therapy thanks to its ability to rejuvenate the skin and reduce the typical signs of ageing such as the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
This form of light therapy can be extremely effective for all sorts of skin concerns, so in this article Melissa Wilson, practice manager at Skin Inspection, discusses the ins and outs of what phototherapy really is and who it can help.
What is phototherapy?
The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of different types of ultraviolet (UV) light, which is produced by the sun. This UV light is used as part of a phototherapy treatment as the strengths and levels of it can be controlled in order to be most beneficial to you. Ultraviolet light B (UVB) has a medium wavelength that is capable of reaching the top layer of your skin, whilst ultraviolet light A (UVA) can reach the first two layers of your skin and therefore goes much deeper.
UV light is known to have an effect on the immune system and is particularly good in reducing the inflammatory response that is seen in many skin conditions.
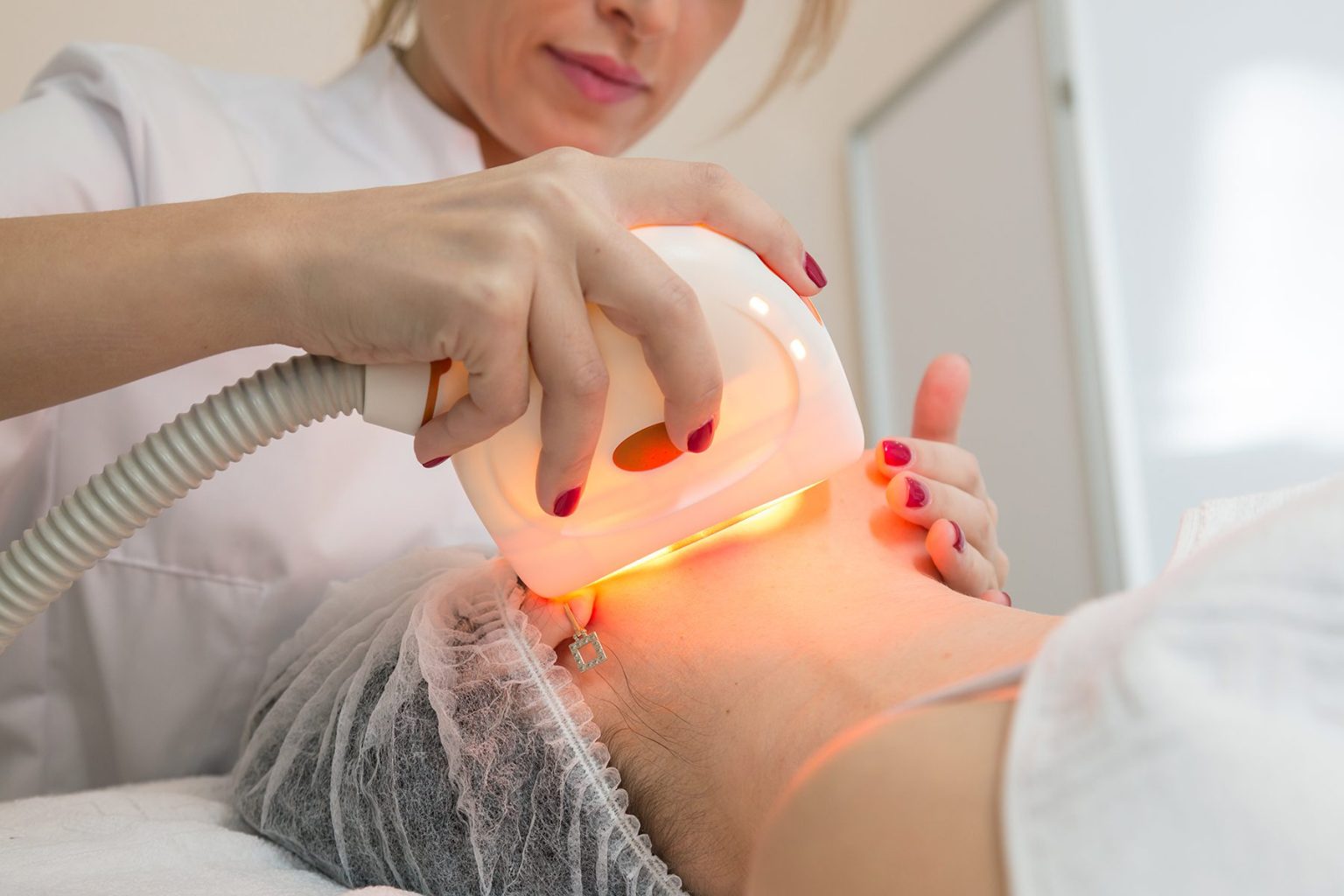
Phototherapy lights use two different colours, with each one working best for different skin conditions. Blue LED lights are used for issues such as jaundice, whilst red LED lights are known to be effective in reducing wrinkles, redness, scars and acne.
What happens during a phototherapy treatment?
A phototherapy treatment can be quite a relaxing experience, and usually does not last long. Phototherapy can be delivered in a number of ways depending on the area to be treated, and so could take the form of a full body chamber, a handheld wand or a mask. You will then be required to remain still for a few minutes with your eyes protected, while the light is applied.
The intensity of the light and the frequency of your treatment will depend on what your skin concern is and the severity of it.
How does phototherapy work?
Phototherapy works by reducing growth of skin cells and treating underlying inflammation by exposing the skin to an Ultra Violet (UV) light for a certain amount of time. The UV light will shut down the immune system cells that are on an area of skin affected by certain types of skin conditions that are caused by the overreaction of the immune system. Such as eczema or psoriasis for example. By stopping the immune system cells, phototherapy helps to ease the symptoms and reduce the appearance of these conditions.
What can phototherapy be used to treat?
Phototherapy is known to be effective in treating a wide range of skin conditions, including things such as psoriasis, eczema and vitiligo. As it can reduce inflammation, it is particularly useful for any conditions which produce symptoms of itching or redness.
Blue light phototherapy has been found to be beneficial for those with acne as it can not only help with the inflammation, but it can also be used to kill the bacteria that is on the skin as the light has an antimicrobial effect. It does this by removing excess oils and dead skin cells from clogged pores which can result in clearer skin.
It is important to remember that overexposure to any form of UV light can lead to burns, skin damage, premature ageing and even skin cancer, so this needs to be managed by a professional. The treatment can be incredibly effective at treating a wide range of issues when in the right hands and can provide a solution that other topical treatments have not been able to offer.
Who can have phototherapy?
Phototherapy can be an option for anyone if a healthcare professional has recommended it. This treatment is suitable for both children and adults, and it is even used in some cases of newborn jaundice. However, certain factors may influence whether light therapy is appropriate for you. It’s crucial to inform your healthcare provider if you:
- Have a sun allergy.
- Have a history of skin cancer.
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Have liver disease.
- Have lupus.
- Have a genetic condition that increases your susceptibility to sun damage, such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Are taking medication that increases your sensitivity to sunlight.
Why choose phototherapy?
Phototherapy can be an excellent choice for treating a range of skin conditions. A dermatologist may recommend phototherapy to patient when you have an allergy to certain topical treatments. In instances such as these, phototherapy can be an excellent choice as it requires no creams or moisturisers be applied to the skin, therefore avoiding any adverse reactions that you may have to the treatment.