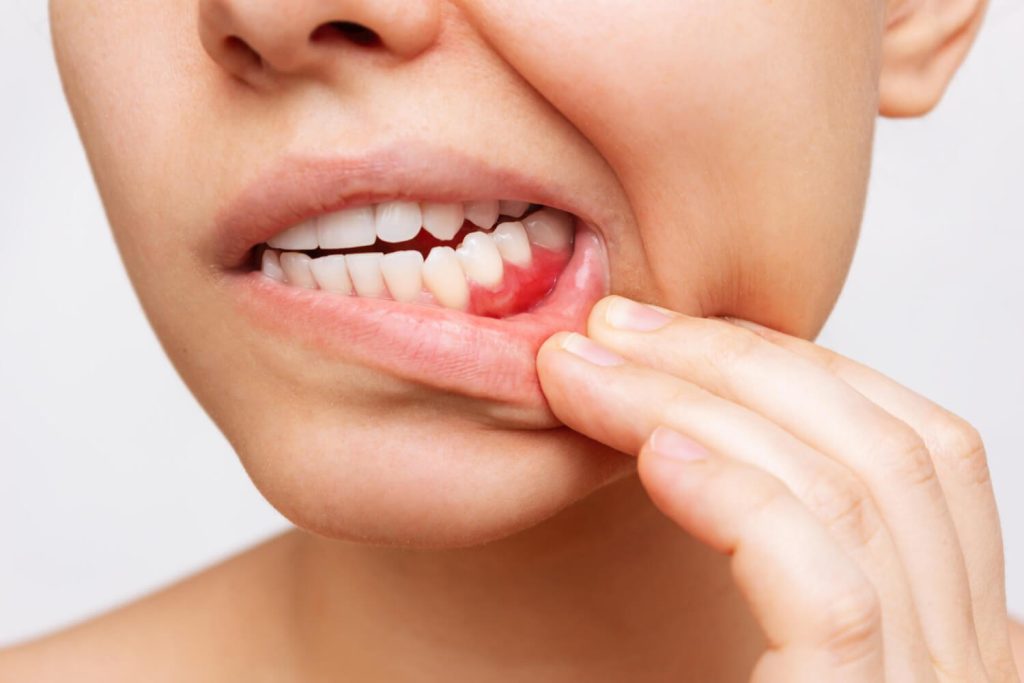
In the realm of dental health, the relationship between inflamed gums and tooth sensitivity is a topic of great importance and concern. When it comes to maintaining a healthy smile, understanding the interplay between these two factors is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, aim to shed light on this dental conundrum, providing you with valuable insights that can help you navigate the complex world of oral health.
Understanding Inflamed Gums
Inflammed gums, also known as gingivitis, is a common dental condition characterized by the inflammation of the gums surrounding your teeth. This inflammation is often accompanied by redness, swelling, and tenderness. While gingivitis is generally not painful, if left untreated, it can progress to a more severe condition called periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss and other serious oral health issues.
The Link Between Inflamed Gums and Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity, on the other hand, refers to the discomfort or pain experienced when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic substances. This sensitivity occurs when the protective enamel on your teeth becomes compromised, exposing the underlying dentin and nerve endings. But how are inflamed gums and tooth sensitivity connected?
1. Receding Gums
Inflamed gums can lead to gum recession, a condition where the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth. As the gums recede, they expose the sensitive dentin beneath, making your teeth more susceptible to sensitivity. This exposure can occur due to the inflammation weakening the gum’s attachment to the tooth.
2. Erosion of Enamel
Inflamed gums often coincide with poor oral hygiene habits. The presence of bacteria and plaque on the teeth can contribute to enamel erosion. As the enamel wears away, the dentin layer is left exposed, resulting in heightened tooth sensitivity.
3. Tooth Grinding
In some cases, individuals with inflamed gums may unconsciously grind their teeth, especially during sleep. This grinding action can further exacerbate tooth sensitivity by wearing down the enamel.
Addressing the Issue: How to Alleviate Inflamed Gums and Tooth Sensitivity
Now that we’ve established the connection between inflamed gums and tooth sensitivity, it’s crucial to explore effective strategies to address these concerns.
1. Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene
A rigorous oral hygiene routine is the first line of defense against both inflamed gums and tooth sensitivity. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash. Regular dental check-ups are also essential for early detection and intervention.
2. Use a Desensitizing Toothpaste
Desensitizing toothpaste contains active ingredients that help block nerve signals in the teeth, reducing sensitivity. Consult your dentist to determine the most suitable desensitizing toothpaste for your specific needs.
3. Treat Inflamed Gums
To address inflamed gums, it’s essential to consult a dentist or periodontist. They can recommend appropriate treatments, such as professional cleanings, scaling and root planing, or antibiotic therapy, depending on the severity of your condition.
4. Wear a Nightguard
If you grind your teeth at night, wearing a custom-made nightguard can protect your teeth from further enamel erosion and alleviate tooth sensitivity.
Conclusion
In summary, the relationship between inflamed gums and tooth sensitivity is undeniable. Inflamed gums can contribute to tooth sensitivity through gum recession, enamel erosion, and tooth grinding. However, with proper oral care and timely intervention, you can manage and even prevent these issues.
Remember, your oral health is a critical component of your overall well-being. Don’t ignore the signs of inflamed gums or tooth sensitivity. Seek professional dental care and follow a consistent oral hygiene routine to maintain a healthy, pain-free smile.